PDR Process: Boosts Vehicle Resale Value Significantly

The PDR process revolutionizes car bodywork repairs, restoring vehicles to pre-damage condition with…….
In today’s rapidly evolving world, the concept of Progressive Development and Regulation (PDR) has emerged as a powerful framework shaping various industries and global initiatives. This article aims to delve into the intricate details of the PDR process, exploring its impact, challenges, and future potential. By understanding this methodology, we can uncover strategies to drive sustainable growth, enhance innovation, and address complex global issues. The PDR process is not merely a set of guidelines but a holistic approach that fosters progress while ensuring responsible practices.
Definition:
Progressive Development and Regulation (PDR) is an innovative methodology that promotes sustainable development by integrating development initiatives with robust regulatory frameworks. It emphasizes a dynamic and adaptive approach to address complex socio-economic challenges, ensuring long-term viability and inclusivity.
Key Components:
Progressive Development: This involves a phased implementation strategy where basic infrastructure and services are initially provided, followed by gradual enhancements and the introduction of advanced technologies or systems. For example, in rural areas, starting with access to clean water and electricity, then introducing digital connectivity and modern farming techniques.
Regulatory Framework: PDR relies on well-designed regulations that adapt as development progresses. These rules ensure environmental sustainability, consumer protection, fair competition, and adherence to social responsibilities. For instance, implementing emission standards for industries as they expand or setting guidelines for data privacy as digital infrastructure grows.
Stakeholder Engagement: Active participation of local communities, businesses, governments, and international organizations is essential. This collaborative approach enables tailored solutions, fosters ownership, and enhances the long-term success of development projects. Community consultations, public-private partnerships, and multi-stakeholder platforms are common engagement mechanisms.
Historical Context:
The PDR process has evolved over several decades, drawing inspiration from various developmental theories and practices. Initially, top-down approaches focused on rapid industrialization and infrastructure development without adequate consideration for environmental or social impacts. As a response, bottom-up initiatives emerged, emphasizing community involvement and sustainability. The modern PDR approach combines these perspectives, creating a balanced strategy that respects local contexts while aiming for global standards.
The influence of the PDR process is evident across sectors and regions, shaping economic growth, social welfare, and environmental stewardship.
International Adoption:
Trends Shaping the Future:
Digital Integration: The integration of digital technologies is a significant trend within the PDR framework. Digital connectivity enables efficient service delivery, data-driven decision-making, and enhanced stakeholder engagement. Smart cities, e-governance, and digital financial services are gaining traction globally.
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): The UN’s SDGs have played a pivotal role in shaping the PDR agenda. Countries worldwide are aligning their development strategies with these goals, focusing on eradicating poverty, promoting equality, and protecting the environment. The PDR process provides a practical framework to achieve these ambitious objectives.
Climate Resilience: With growing climate concerns, building resilience against natural disasters and environmental changes is a significant trend. PDR initiatives incorporate climate-smart strategies, such as sustainable agriculture practices, renewable energy adoption, and resilient infrastructure development.
The PDR process has profound implications for economic systems and market dynamics.
Market Dynamics:
Investment Patterns:
Role in Economic Systems:
The PDR process contributes to economic stability and growth by:
Reducing Inequalities: Through targeted interventions and inclusive policies, PDR aims to narrow the wealth gap, ensuring that development benefits all segments of society.
Promoting Financial Inclusion: Access to financial services, digital banking, and microfinance initiatives under the PDR umbrella empower low-income groups, enabling them to participate in the economy.
Encouraging Innovation: By fostering a supportive regulatory environment, PDR encourages innovation, leading to new products, services, and business models that drive economic growth.
Technology plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of the PDR process, offering both disruptive innovations and enhancements to existing practices.
Disruptive Technologies:
Enhancements and Applications:
The success of the PDR process heavily relies on well-designed policies and regulations that adapt to changing circumstances.
Key Policies:
Environmental Protection Laws: These ensure sustainable resource use, pollution control, and conservation efforts. Examples include emissions standards, waste management regulations, and protected area designations.
Consumer Protection Acts: Safeguarding consumers’ rights is vital for fostering trust in markets. These policies regulate product quality, pricing, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
Competition Policy: Promoting fair competition among businesses prevents monopolies and fosters innovation. Antitrust laws and regulatory bodies play a crucial role here.
Regulatory Frameworks:
Despite its numerous advantages, the PDR process faces several challenges and criticisms that require careful consideration and strategic solutions.
Main Challenges:
Lack of Political Will: Insufficient commitment from governments can hinder progress, especially in implementing long-term development strategies and regulatory reforms.
Inequalities and Social Disparities: PDR must address existing inequalities to ensure that development benefits all segments of society. This includes efforts to empower marginalized communities and close the digital divide.
Regulatory Burdens vs. Flexibility: Striking a balance between robust regulations and flexibility is crucial. Overly stringent rules may hinder innovation, while insufficient regulation can lead to exploitation or environmental degradation.
Strategies for Overcoming Issues:
The successful implementation of the PDR process is evident in various case studies across different regions, each offering valuable lessons.
Case Study 1: Smart City Development in Singapore:
Singapore’s transformation into a smart and sustainable city showcases the PDR approach. The government engaged stakeholders to develop a comprehensive digital masterplan, improving urban services and infrastructure. This included implementing efficient public transport systems, smart energy grids, and advanced waste management solutions. The result is a livable, environmentally conscious metropolis that attracts global talent and investments.
Case Study 2: Rural Electrification in Africa:
In rural areas of Kenya, the PDR process has been instrumental in providing electricity to communities previously reliant on firewood or kerosene. A public-private partnership successfully deployed solar panels and mini-grids, improving living standards and economic opportunities. This case highlights the progressive aspect of PDR, where basic services are initially provided, followed by enhanced infrastructure and digital connectivity.
Case Study 3: Sustainable Tourism in Costa Rica:
Costa Rica’s tourism industry exemplifies how PDR can promote sustainable development. The country implemented strict environmental regulations, protected vast areas as national parks, and invested in eco-tourism infrastructure. This approach attracted ecotourists while ensuring the preservation of natural resources for future generations. The case demonstrates how PDR can drive economic growth while maintaining ecological integrity.
The PDR process is poised for further evolution, driven by emerging trends and technological advancements.
Potential Growth Areas:
Emerging Trends:
Circular Economy: This concept focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing resource value. PDR can facilitate the transition by regulating recycling practices, promoting product design for longevity, and fostering circular business models.
Genetic Technologies: Advances in genetic engineering and biotechnology have immense potential. PDR must navigate ethical considerations while embracing these technologies for improved food security, medicine, and environmental conservation.
Data Governance: With the exponential growth of data, effective data governance frameworks are essential. PDR can shape data protection regulations, ensure digital rights, and facilitate responsible data sharing.
Strategic Considerations:
The PDR process serves as a powerful catalyst for driving sustainable development, fostering innovation, and building resilient communities worldwide. By integrating development with robust regulations, this approach ensures that progress is measured not only by economic growth but also by environmental stewardship and social equity. As the world navigates complex challenges, from climate change to digital transformation, the PDR process offers a comprehensive framework for navigating the future.
By embracing the principles of progressive development, stakeholder engagement, and adaptive regulation, nations can unlock their full potential. The case studies presented in this article highlight successful applications, demonstrating the transformative power of PDR. As we look ahead, the future prospects section offers insights into emerging trends and strategic considerations, guiding us toward a sustainable and prosperous global landscape.
Q: How does PDR balance economic growth with environmental sustainability?
A: PDR promotes sustainable development by integrating environmental regulations into economic strategies. This ensures that economic growth is not at the expense of natural resources but rather enhances them for future generations.
Q: What role do local communities play in the PDR process?
A: Local communities are active participants, ensuring that development priorities reflect their needs and aspirations. Their involvement fosters ownership and facilitates more inclusive and effective project implementation.
Q: How can technology enhance the PDR process?
A: Technology enables efficient service delivery, data-driven decision-making, and enhanced stakeholder engagement. Disruptive technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain have the potential to revolutionize various aspects of development and regulation.
Q: What are some common challenges faced in implementing PDR?
A: Challenges include political will, social disparities, and regulatory burdens. Overcoming these requires strong leadership, inclusive policies, and adaptive regulation that learns from experience and incorporates new insights.
Q: Can you provide examples of successful PDR initiatives worldwide?
A: Indeed! Singapore’s smart city development, Kenya’s rural electrification projects, and Costa Rica’s sustainable tourism initiatives are notable examples. Each demonstrates the successful application of PDR principles in different contexts.

The PDR process revolutionizes car bodywork repairs, restoring vehicles to pre-damage condition with…….

Despite emerging technologies, Paintless Dent Repair (PDR) remains a preferred and effective method…….

The PDR process is a non-invasive car restoration technique using specialized tools to remove dents…….
The PDR process is a specialized automotive repair technique for preserving factory paint finishes b…….

The initial stage of the PDR process is crucial, focusing on detailed inspections, customer consulta…….
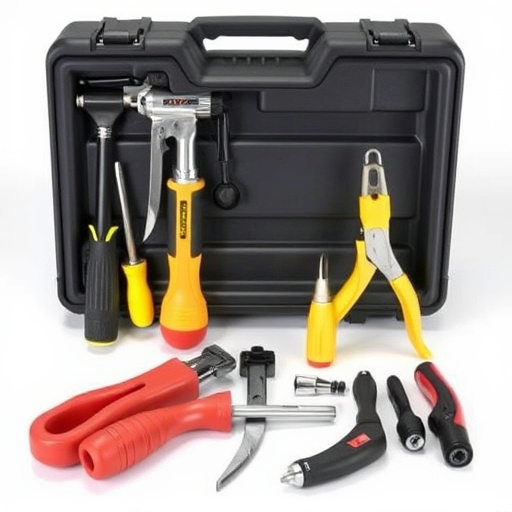

The PDR process is ideal for modern cars with smooth body panels in cool, shaded areas, treating min…….

The PDR process (Paintless Dent Repair) is a game-changer in automotive dent repairs, offering swift…….

In a competitive auto collision industry, PDR (Paintless Damage Repair) training enhances efficiency…….

Automotive professionals skilled in Paintless Dent Repair (PDR) offer efficient, cost-effective coll…….

The PDR process revolutionizes automotive repairs by offering efficient, cost-effective solutions fo…….